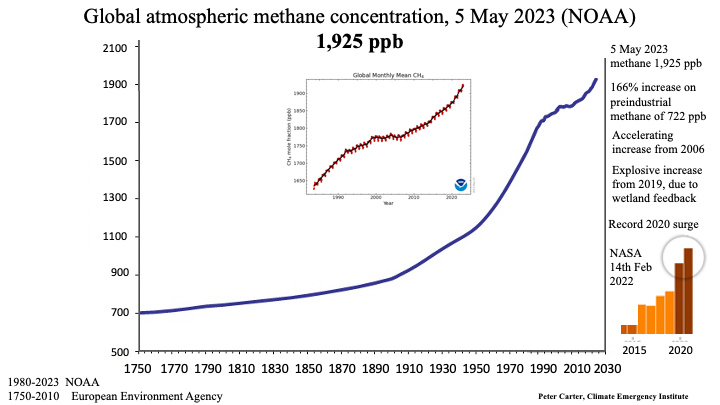
Climate change indicators: record high
increasing at record rates
GLOBAL EMISSIONS HAVE TO DECLINE RAPIDLY ON AN IMMEDIATE BASIS
For both the 1.5°C and 2.0°C limit (IPCC, 2022, AR6)
Keynote address by the IPCC Chair Hoesung Lee at the opening of COP26 Glasgow, 31 October 2021
"Global warming of 1.5°C and 2°C will be exceeded during this century unless immediate, rapid, and large-scale reductions in greenhouse gas emissions, especially of carbon dioxide and methane occur "
All it takes
GOVERNMENTS MUST STOP FOSSIL FUEL FUTURE-DESTROYING SUBSIDIES.
That Are Increasing !
2020 fossil fuel subsidies were $5.9 trillion or 6.8 percent of GDP
Expected to increase to 2025
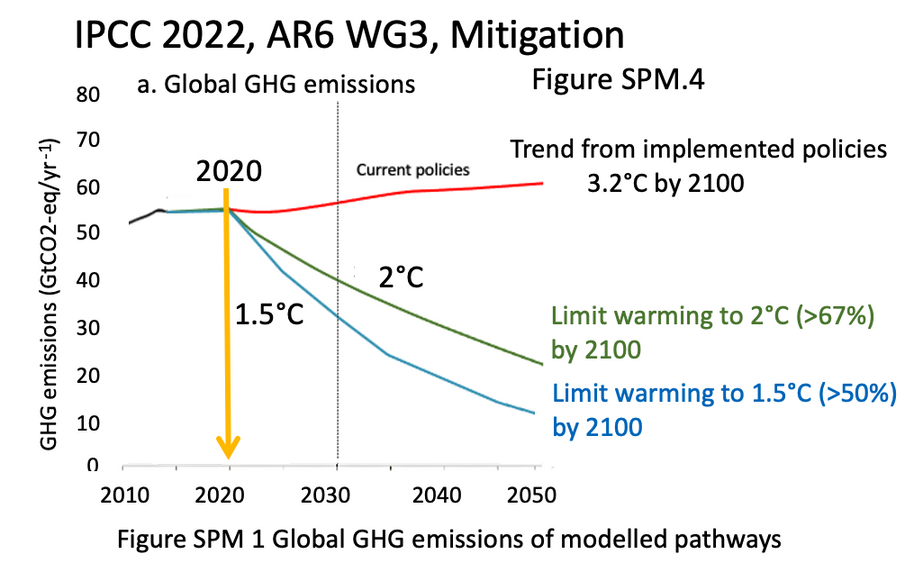
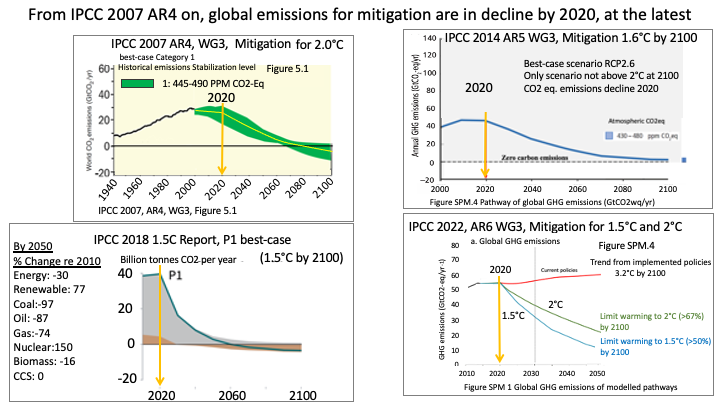
Global emissions had to be in decline from 2020
This image from the IPCC 6th assessment shows that global greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions had to be in decline from 2020 to limit global warming to 1.5°C and to 2.0°C (by 2100). If not, according to the IPCC the world would be at 1.5°C in the early 2030's and 2.0°C by 2050. "In all scenarios crossing the 1.5°C threshold lies in the early 2030s” (IPCC AR6 WG1 Ch.4-555)
The IPCC 2018 1.5°C report is what led to the world recognizing the global climate emergency, and to the scientists and policy makers changing the global warming limit from 2.0°C (the limit since the 1990s) to 1.5°C.
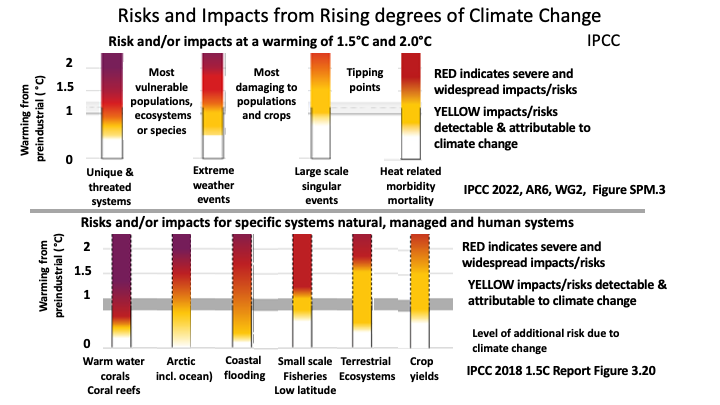
While 1.5°C is globally disastrous, 2°C would be total global climate catastrophe leading to uncontrollable rapid heating.
1.5°C is globally disastrous, while 2.0°C would be global catastrophe
For mitigation, in the IPCC 2007 4th Assessment and on, global emissions
declined by 2020 at the latest
BASIC SCIENCE OF THE EMERGENCY: Every increment of warming results in rapidly escalating hazards.
More intense heat-waves, heavier rainfall and other weather extremes further increase risks for human health and ecosystems. Climate-driven food and water insecurity is expected to increase with increased warming (IPCC AR6, SYR 20 March 2023).

The science predicted multiple severe climate change impacts
that would increase with global warming long ago

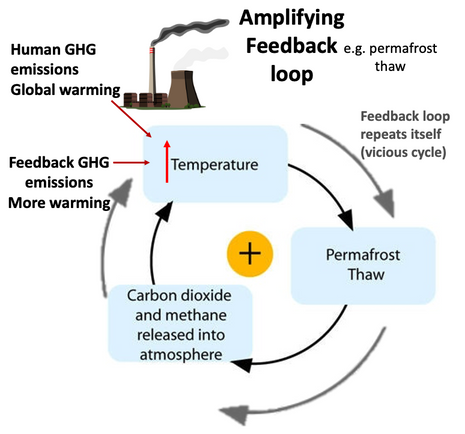
Amplifying feedback loops are the greatest very worst effect of global warming
and are certain at high enough degrees of warming
Albedo Feedback is from loss of cooling (albedo) Arctic summer sea-ice and snow
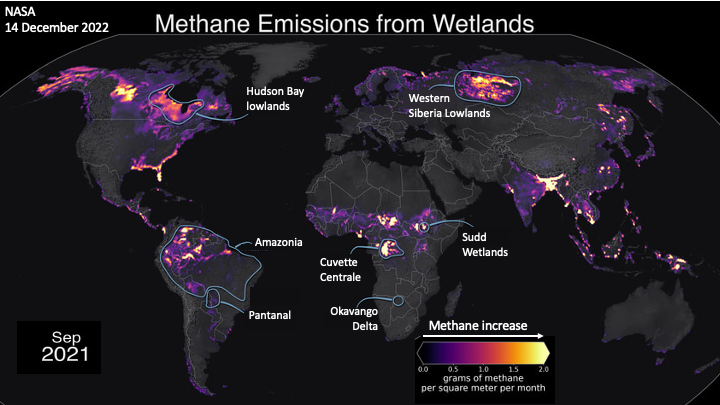
Greenhouse Gas Feedbacks are shown on the map below
Wetland peat and thawing permafrost emit methane, CO2 and also nitrous oxide
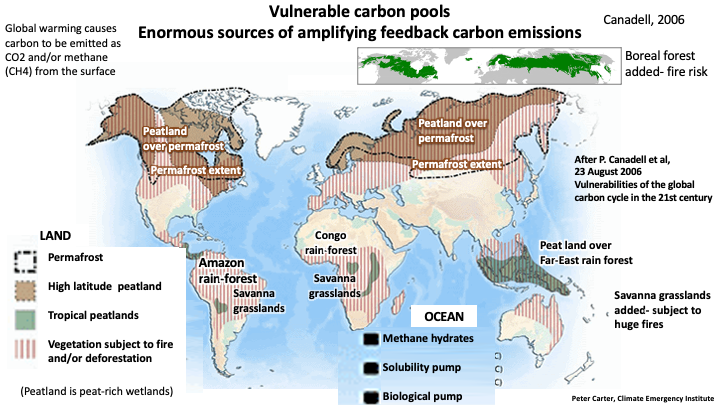
Tropical and Far North wetlands under warming and wetness are emitting more methane as feedback, boosting atmospheric methane faster than ever.
20 March 2022, Recent intensification of wetland methane feedback Zhen Zhang et al